Computational Chemistry
Chemistry that uses computer simulations
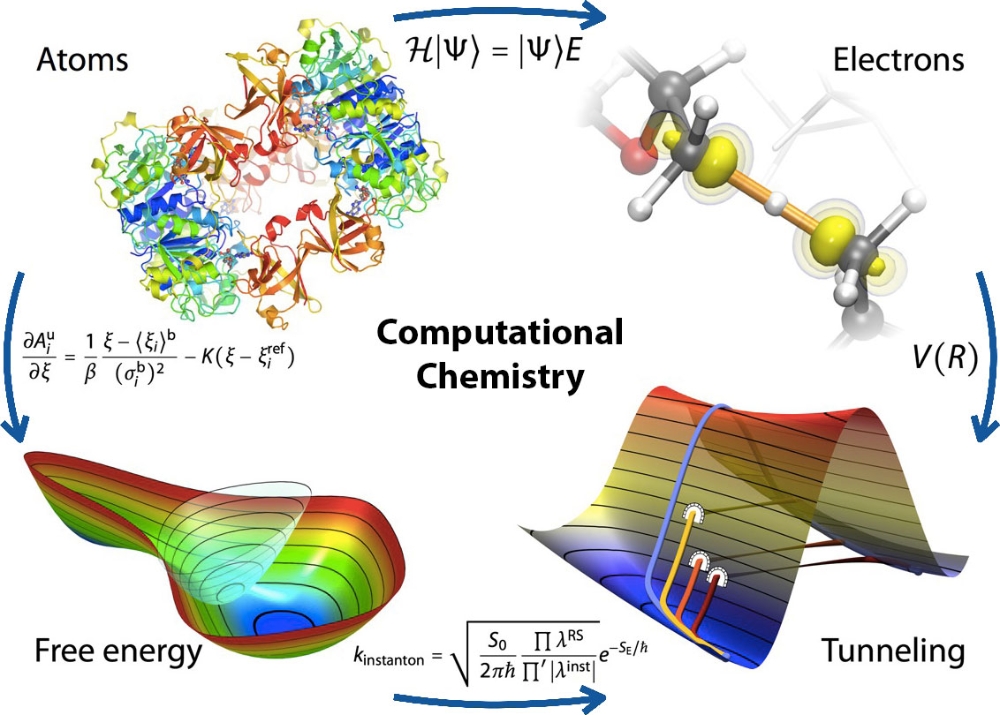
Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry that uses computer simulations to assist in solving chemical problems. It uses methods of theoretical chemistry incorporated into computer programs to calculate the structures and properties of molecules, groups of molecules, and solids. Computational chemistry can also predict unobserved chemical phenomena and explore reaction mechanisms that are difficult to study experimentally. Some applications of computational chemistry include drug design, chemoinformatics, consumer packaged goods, protein engineering, enzyme design, organic electronics, catalysis design, polymer design, surface chemistry, energy capture and storage, and more. Computational chemistry can reduce the time, money, and resources spent on synthesis, assays, and other experimental work by providing accurate and fast predictions of molecular structures and properties.
Learn more on wikipediaCoded by 👩💻 Asandiswa Mfenguza❤️