🧬 Intro to CRISPR-Cas9 🧬
Clustered Regulatory Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeat
CRISPR associated protein 9
What is CRISPR-Cas9?
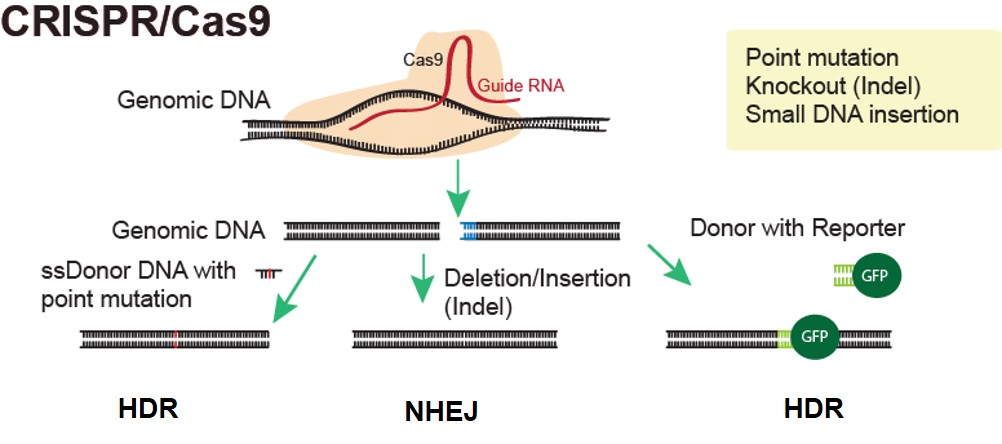
CRISPR-Cas9 is a gene editing tool that allows scientific researchers to alter genomes by adding, deleting or manipulating components of the DNA sequence. It uses Cas9, an enzyme that is able to cut at a specific location in the DNA strands so that components can be added, removed or modified. A strand called guide RNA that consists of 20 complimentary bases long and a scaffold, is then able to accurately locate the location on the genome for the enzyme to cut. Once the cut is made, the cell recognizes damage and the DNA will attempt to repair the strand with the mutation incorporated.

This revolutionary tool is beneficial for treating several medical conditions relating to gene components such as hepatitis B, muscular dystrophy and even certain cancers.
Jennifer Doudna and Emmanuelle Charpentier were the first to discover this revolutionary tool, which ended up winning them the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2020. Humans have simply scratched the surface with CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing, there is still plenty of reasearch to be done.